PostgreSQL-gis Redis-geo BuntDB 性能比拼
[toc]
听说 postgresql 中的 postGIS 在处理经纬度方面速率很快(gist 内部使用的是搜索树,geo 内部使用的是 geohash),所以比较一下,看看 8w 数据量的情况下,哪个快一点。
PostgreSQL(pg)搭建
pg 添加 postGIS 扩展(postGIS 扩展很强大,建议深入学习):
1 | create extension postgis; |
附:Mac 安装 PostGIS 流程:link
pg 创建测试表:
1 | postgres=# create table gis_idx_test(id int, info text, pos geometry) with (autovacuum_enabled=off,toast.autovacuum_enabled=off); |
pg 创建索引(使用 gist 的原因是:gist 比 RTree 更强大,虽然插入数据慢,但是检索数据快,适合存储空间的数据):
1 | create index idx_gis_idx_test on gis_idx_test using gist (pos); |
插入数据(我这里使用的是 gorm 插入数据,因为 gorm 不支持 geometry 数据格式,所以只能裸写 sql 了^_^; 尴尬):
1 | func InsertPostgresWithIdAndValue(id int, longitude, latitude float64) { |
共 85318 条数据,其实算是比较少了。
pg redis buntdb 性能比较(单条命令时间查询)
pg 查询
1 | SELECT * FROM gis_idx_test WHERE ST_DWithin(pos :: geography, ST_GeomFromText ( 'POINT(112 -7)', 4326 ) :: geography, 200000) IS TRUE; |
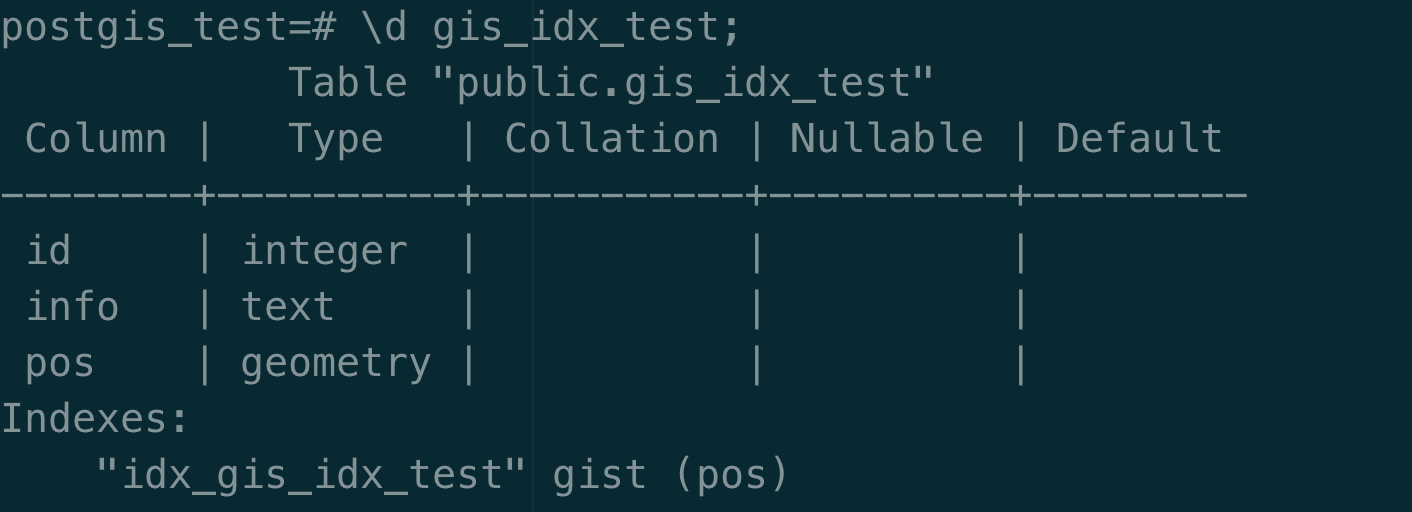
使用explain (analyze,buffers)即可查看 pg 查询时间
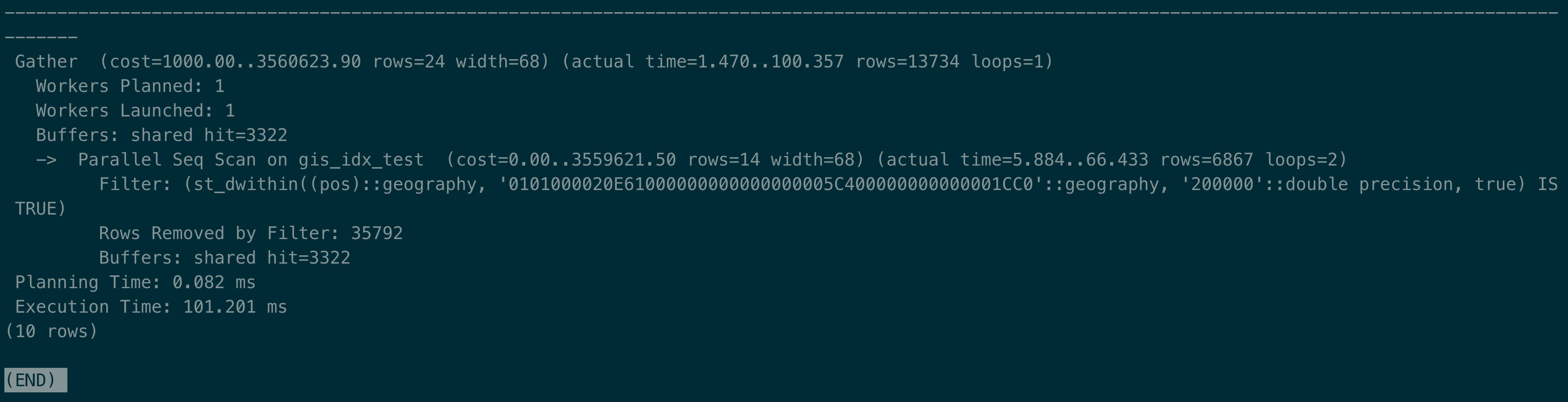
redis 设置 slowlog 并查询时间
1 | redis查询命令:georadius outlet 112 -7 200 km withdist |
明显可以看出查询单次数据,redis 的性能是要远高于 pg 的,大概差距为 5 倍(101ms&19.2ms)。
buntdb 查询
buntdb 链接。如果对数据库感兴趣,不妨先学学这个,麻雀虽小,五脏俱全:
1 | func GetBuntdb() (index int) { |
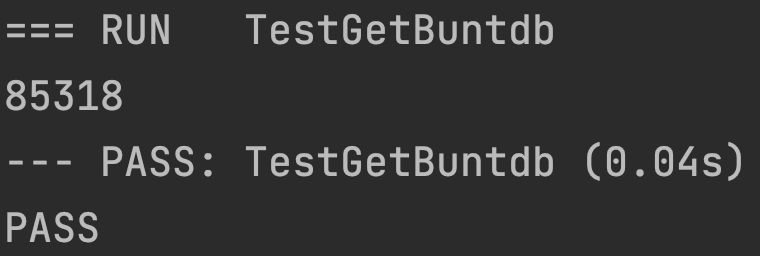
同样也是 8w 多条数据,虽然 buntdb 全盘扫描,但是速度不慢,40ms。
使用 wrk 压测比较 Qps
首先测试保证 redis&pg 执行后的结果是一致的
redis
pg
它两差2个差别其实是因为这两个数据库的存储数据的方式不同,pg 的会更加准确。
(其实在这里明显能看出来,只执行一个明显 redis 速度快的多,因为 redis 是基于内存的…而且数据量小,发挥不出 pg 的优势,hash 数据量大了执行速度就慢了,但平衡多叉树的效率O(n*logn),速度不怎么变。)
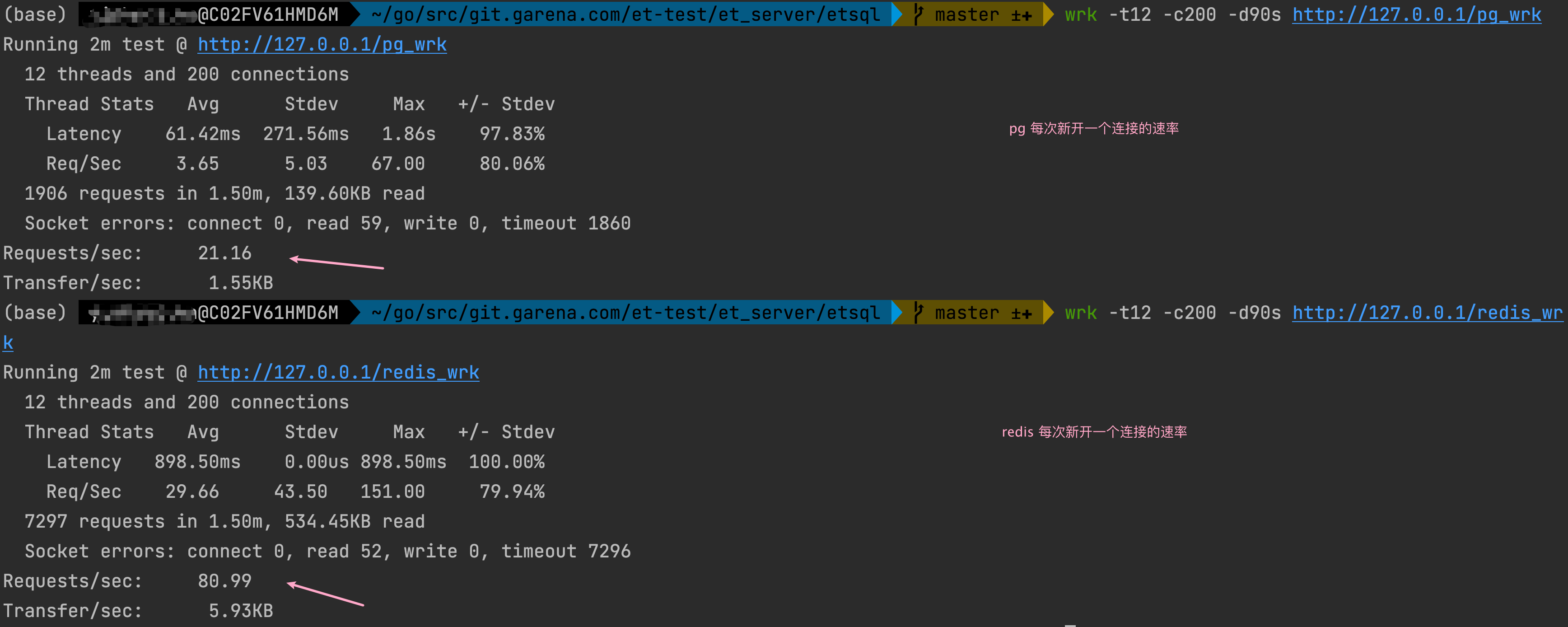
每次 conn 一个连接进行压测
1 | wrk -t12 -c200 -d90s http://127.0.0.1/pg_wrk |
修改 pg 最大链接数:link
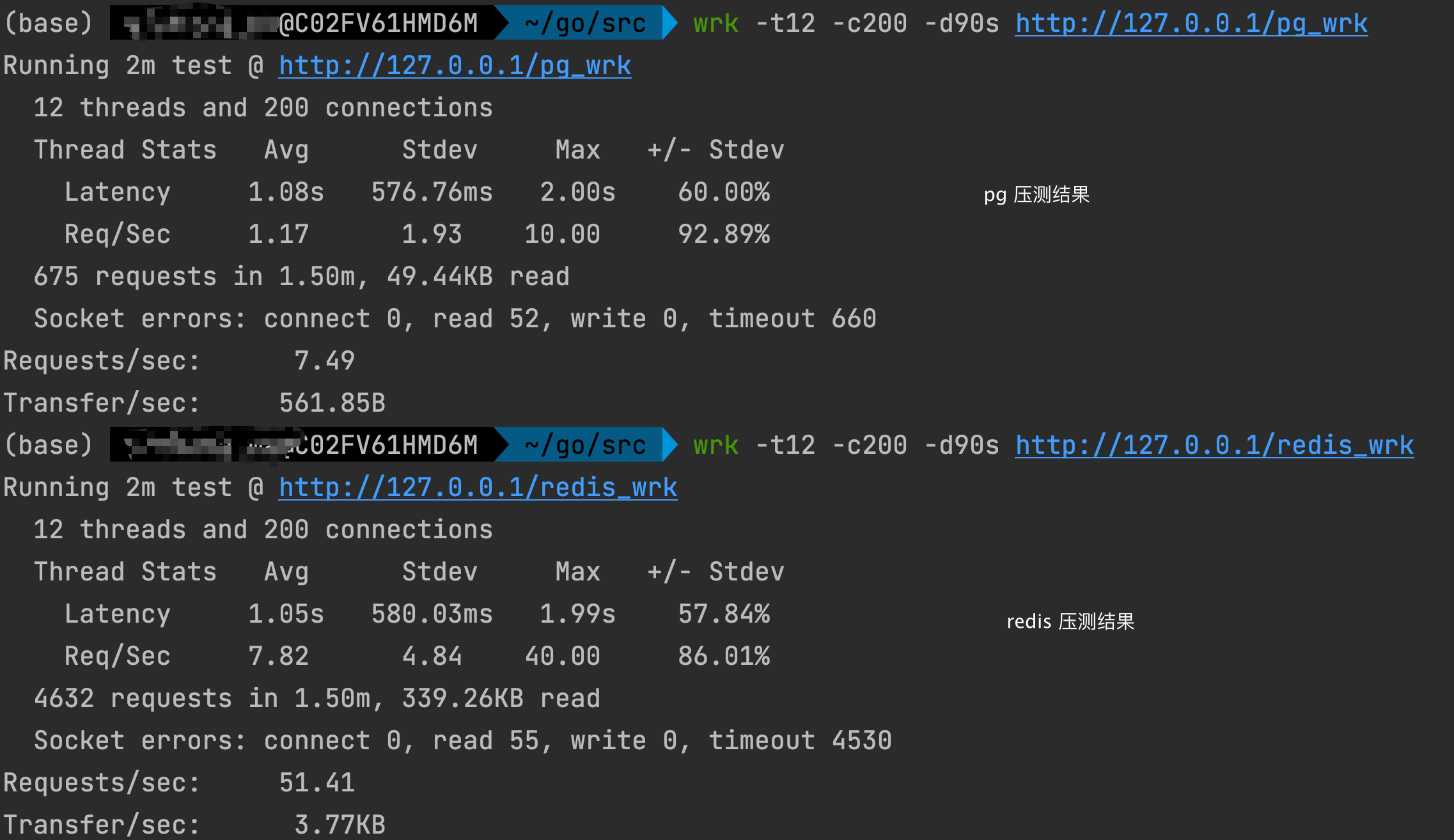
对测试的数据进行加锁压测
初始化好连接的进行加锁压测,保证同时只有一路执行,防止开多个 client 影响速率。
1 | wrk -t12 -c200 -d90s http://127.0.0.1/pg_wrk |
使用连接池压测,模拟真实环境
通过上述结果可以肯定,redis 的速度还是会快一些的。
buntdb 测试
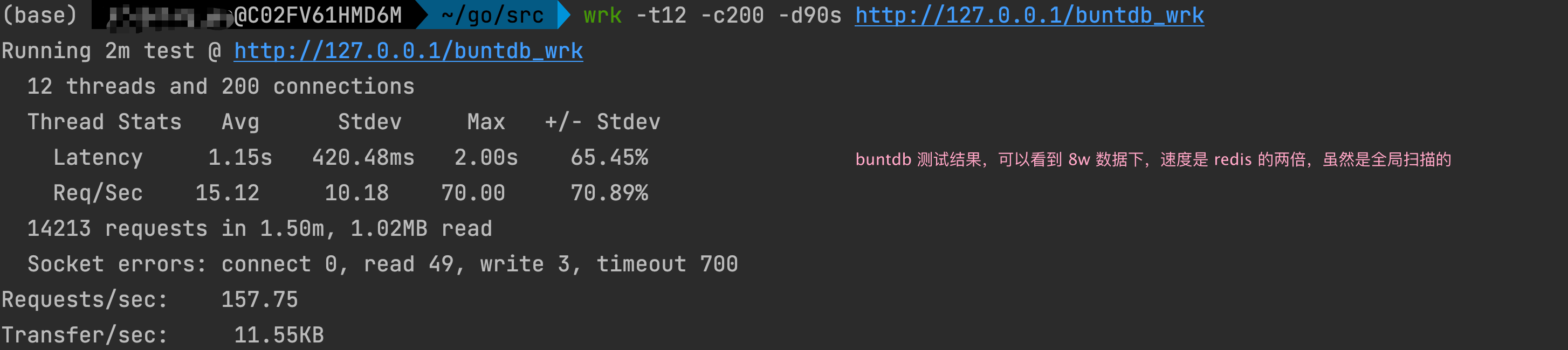
基础测试
可以看出,在 8w 数据量下,速度是 redis 的两倍,虽然 buntdb 是全局扫描的,但是速度并不差。
修改源码后测试
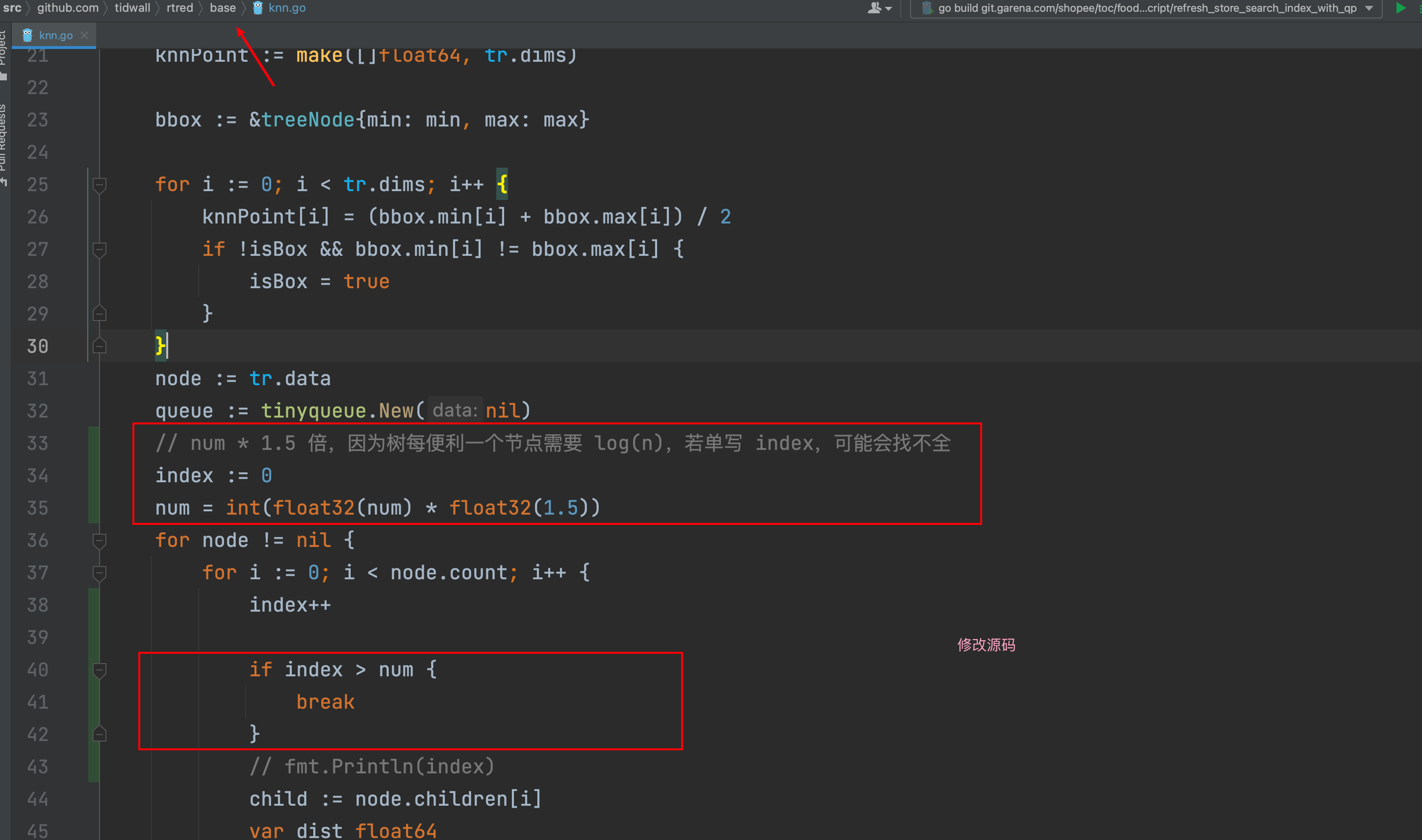
上面的瓶颈主要还是全盘扫描,所以是不是可以不全盘扫描,而直接修改源码只返回部分结果呢,答案是肯定的!
修改如下源码:修改代码链接
测试修改的是否可用
使用命令测试下面函数(buntdb 数据量也是 85318 条)
1 | // 命令:go test -run TestGetBuntdb -v |
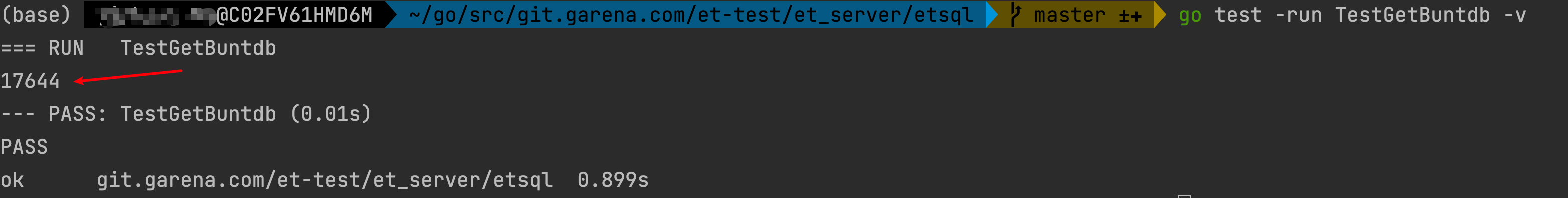
共捞到 17644 条信息,速度是 10ms,很快了。
使用 wrk 进行压力测试如下:
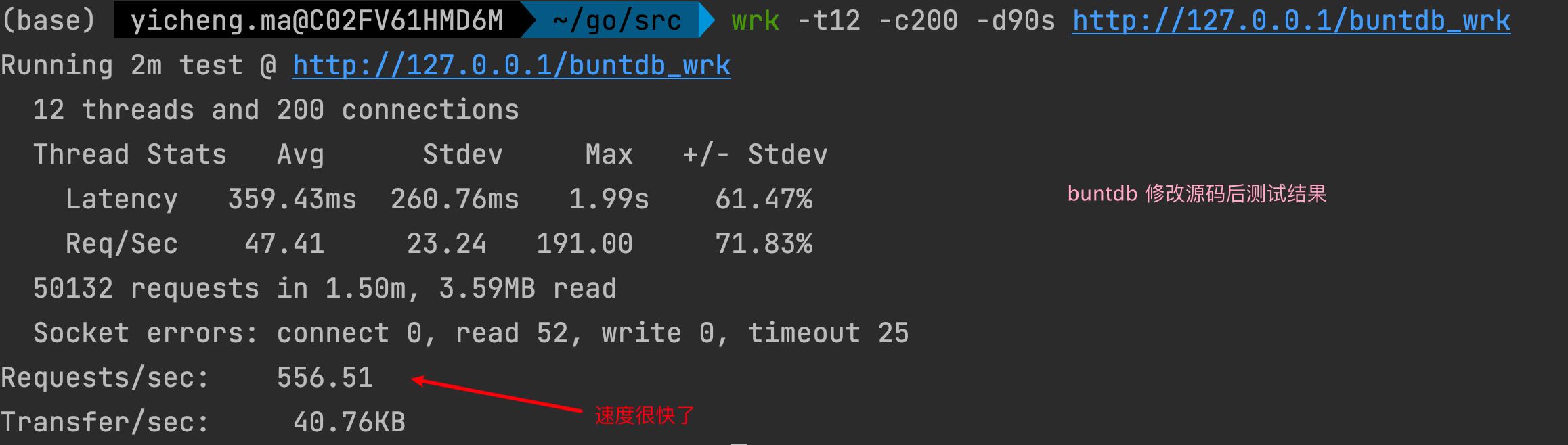
速度是 buntdb 全盘扫描的 2.5 倍,是 redis 的 5 倍。
原始代码单线程执行(和 redis 加锁压测一样)
1 | wrk -t1 -c2 -d30s http://127.0.0.1/buntdb_lock_wrk |
1 | Running 30s test @ http://127.0.0.1/buntdb_lock_wrk |
qps 比并发执行小了 5 倍。
修改代码后单线程执行(同上)
1 | wrk -t12 -c200 -d90s http://127.0.0.1/buntdb_lock_wrk |
1 | Running 2m test @ http://127.0.0.1/buntdb_lock_wrk |
同上,速度慢很多了。
所以可以得出 buntdb 相比 redis-geo 的优势在于
- buntdb读写锁保证可以同时执行,而 redis 单线程
系统资源占用分析
使用 Instruments 进行系统资源占用分析。trance 文件,需要自提
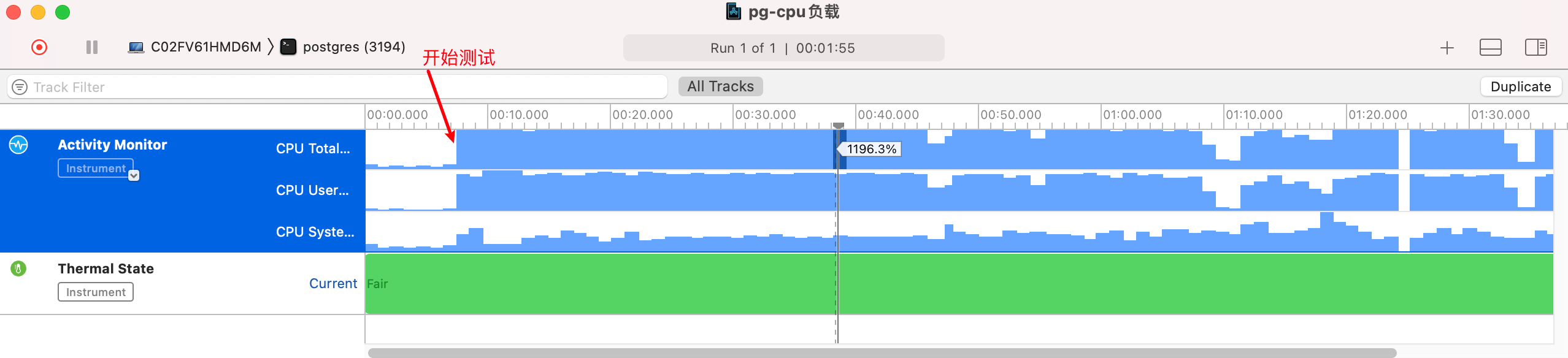
pg
cpu 占用率平均达到了 1200%,太高了。
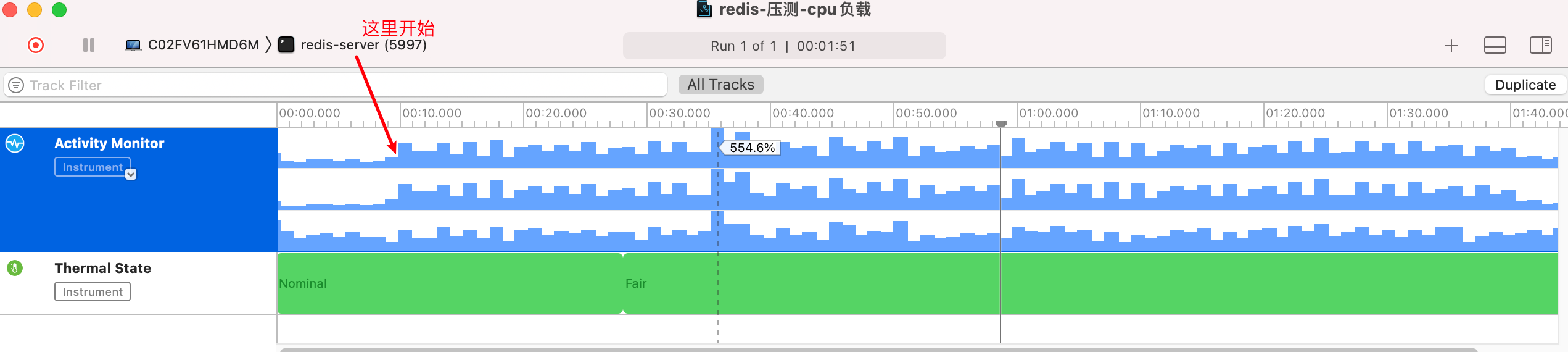
redis
cpu 占用率低多了,最高才 500%。
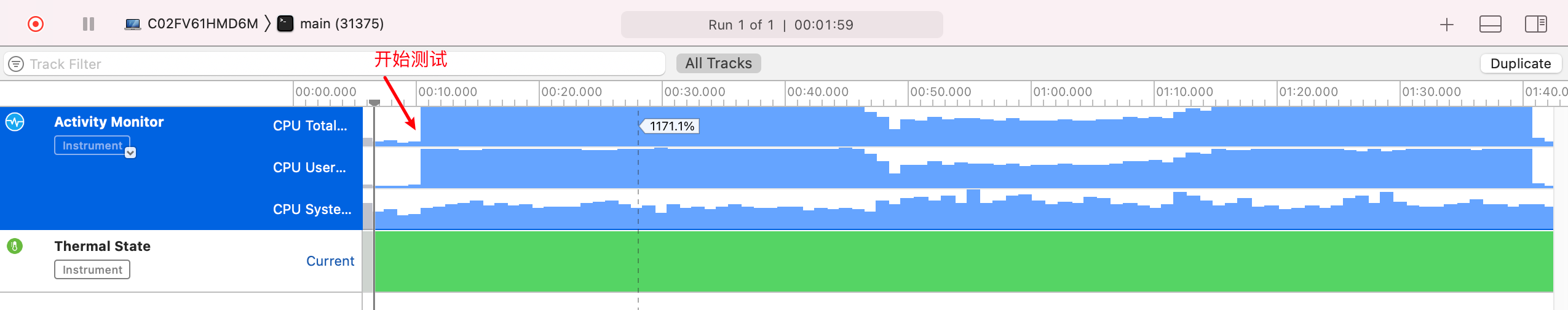
buntdb
cpu占用率很高,毕竟速度快。
内存使用了大约 13 GB。
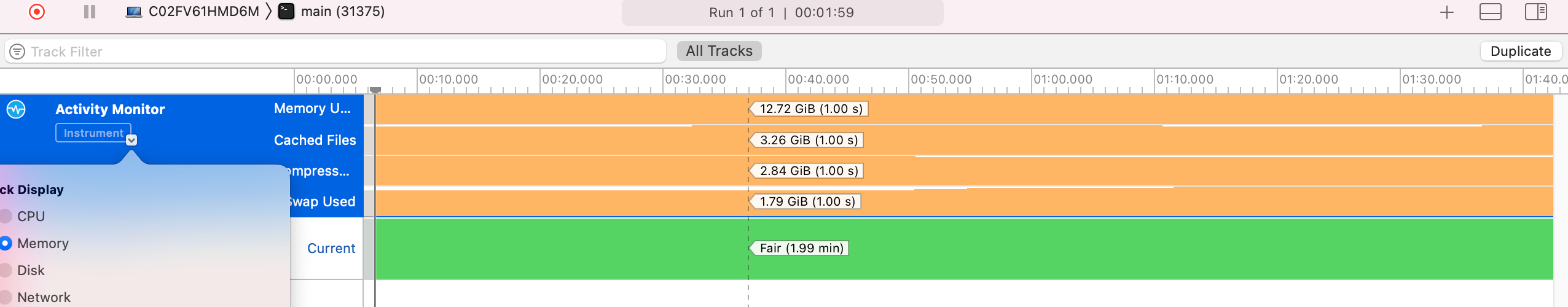
磁盘没怎么用,毕竟 buntdb 文件没多少数据。网络同理(不截图了,费空间)。
总结
在处理地理位置方面,内存型数据库的速度明显优于持久化的数据库。但是一般内存型数据库取到排序后,还需要从持久化数据库取所有数据(这个一般是根据 id 取的,费时间少,但是还是需要列入考虑范围)。
1w-100w 的数据量,获取某点临近位置,使用 buntdb 的速度明显优于 redis(高的数据量没测过,我也不清楚哪个快,但是怀疑 buntdb 快)。
为什么 buntdb 比 redis 快(排名依次减弱)?
- buntdb 使用的是 R-tree,不需要每次 hash 地理位置,而 redis hashgeo 时使用 hash 来计算的(上节已经讲过,redis hashgeo 占总时间的 20%+),所以 buntdb 速度快。
- buntdb 在使用时是读写锁,可以并发执行,并消耗大量 cpu 资源来并发计算。但是众所周知,redis 是单线程(其实可以给 redis 加个线程池,或者多开几个 redis 进行测试,redis 性能还能再快很多,可以看到上面 redis cpu 资源都没怎么费,但是这个测试没必要)。
- redis 需要将拿到的数据传输给 server(1.5分钟 5000w 的数据量),相对也是很费资源的。
优化:
虽然 buntdb 很快,但如果数据量过大,buntdb 速度也是会下降的。
所以思考是否可以首先通过 hashgeo (4-7次 hashgeo)过滤获取一个大的范围,然后将不同的范围的数据,存储到不同的 buntdb 中(看业务,4-7次 hashgeo 分的相当粗,除非特别需求,大部分业务不需要考虑临近问题)。取的时候先 hashgeo,然后从对应的 buntdb 中取就可以了。思路链接
本质上就是分片,不过是分片方式是 geohash 而已
参考
https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/108557/advantages-of-r-trees-in-comparison-to-geohashes
https://www.oschina.net/p/postgis?hmsr=aladdin1e1
http://www.jandrewrogers.com/2015/03/02/geospatial-databases-are-hard/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12492065/how-does-mongodb-implement-its-spatial-indexes/12494924
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/590349
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/179209
https://morphocode.com/how-to-install-postgis-on-mac-os-x/
http://www.mathcs.emory.edu/~cheung/Courses/554/Syllabus/3-index/R-tree.html
https://github.com/digoal/blog/blob/master/201708/20170820_01.md