redis geo 性能分析及对问题的思考
[toc]
对 redis 进行压力测试
将数据存入 redis 后(共 85318 条有效数据),通过压测工具redis-benchmark对 redis 进行压测。
1 | redis-benchmark -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 -c 50 -n 1000 -q georadius outlet 112 -7 200 km withdist |
并发数为 50,每个并发发送 1000 个请求,结果如下:

注:本文所用电脑为 MacBook Pro (16-inch, 2019),cpu 为:Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-9750H CPU @ 2.60GHz,内存为 16 g。
对 redis 进行满载压力分析
使用 Instruments 对 redis 进行满负荷时分析,压力测试命令如下:
1 | redis-benchmark -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 -c 100 -n 50000 -q georadius outlet 112 -7 200 km withdist |
说几点建议:
- 多开几个压测的线程,多个线程并发执行,尽可能的去打满 redis,以遍更直观的看到 redis 的性能瓶颈。
- 有条件的可以使用两个本地机器去模拟(必须为局域网,
当然两根网线连着更好,非局域网可能会有网速对 redis 性能的影响),使用同一台电脑开启 redis 服务和进行压测时,压测开很多线程,一直发数据也是很消耗 cpu 资源的(这个东西属于 unstable,看内核调度,是不可控的)。所以为了控制变量,让 redis 能更好的发挥效率,推荐使用两个机器。
满负荷执行两分钟的结果如下(性能分析的 trace 文件,需要的自提):
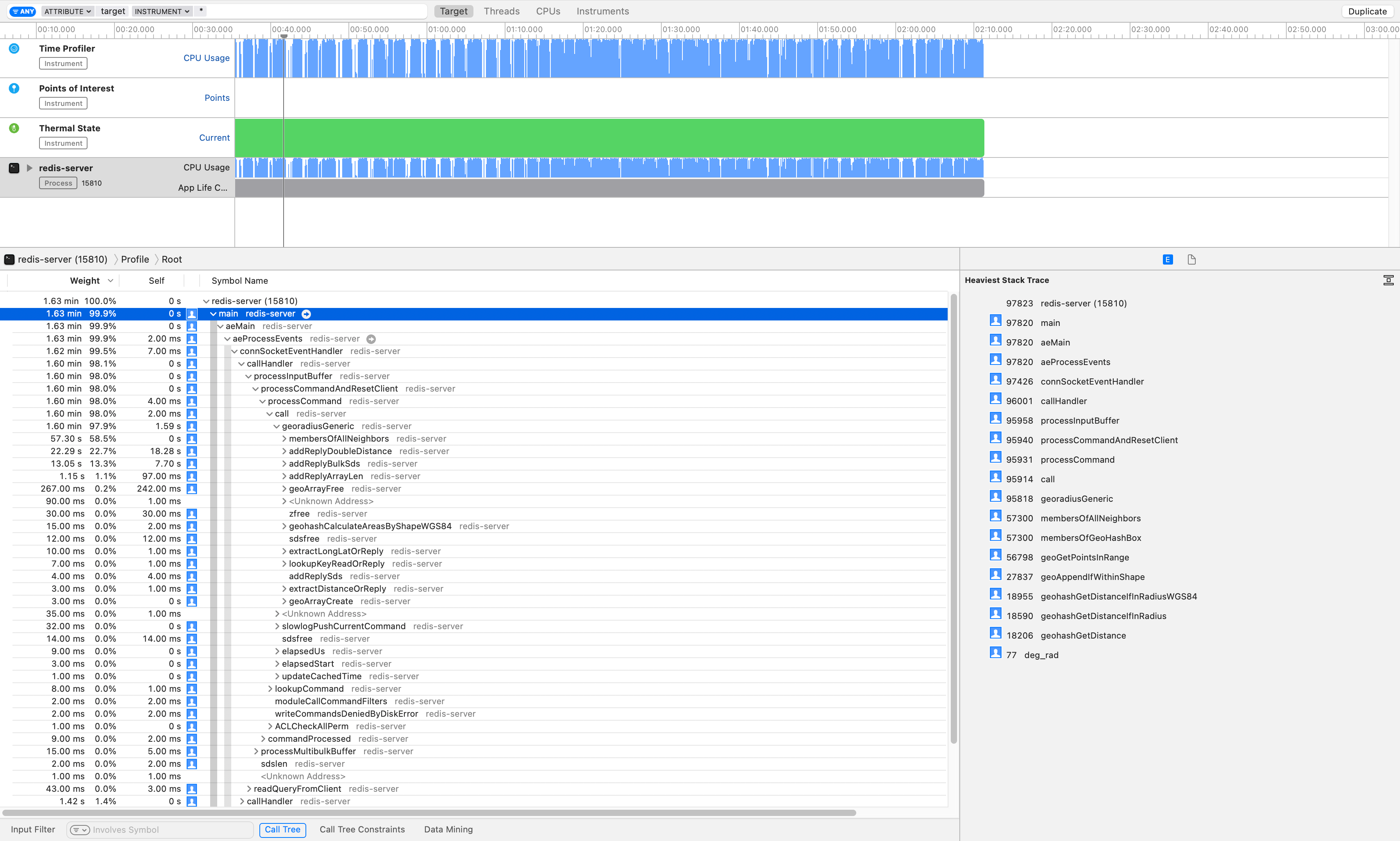
注:强烈推荐使用 Linux 系统的 perf 对 redis 进行性能分析,虽然 mac 分析的很全面,但是生成不了火焰图导致结果很不直观,需要手动一条一条找数据。好在数据量不大,因此逐个分析吧(这是网上仅有的 mac 生成火焰图的方式链接,但是我没有测试成功)。
georadiusGeneric
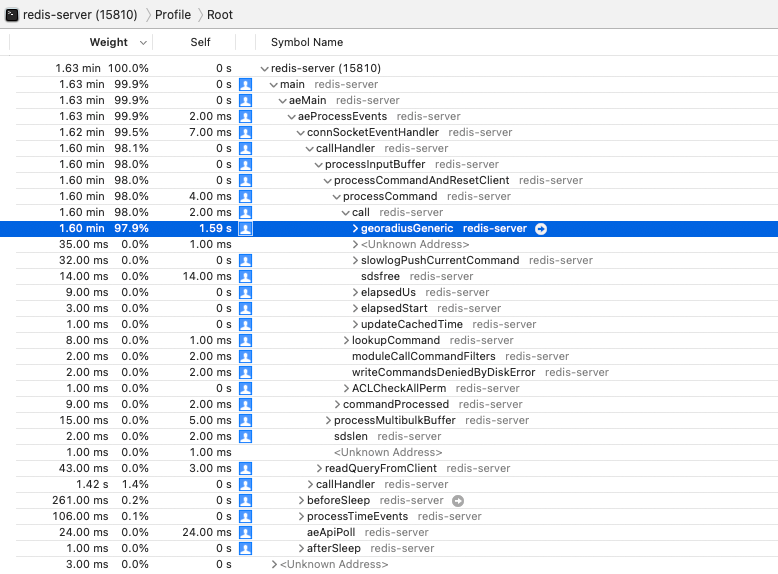
可以看出 97.9% 的时间都花费在了这个函数上,这个函数其实就是一个回调,执行 georadius 的命令。
1 | /* GEORADIUS wrapper function. */ |
这个命令下共有 3 个函数费时间,下面依次进行分析。
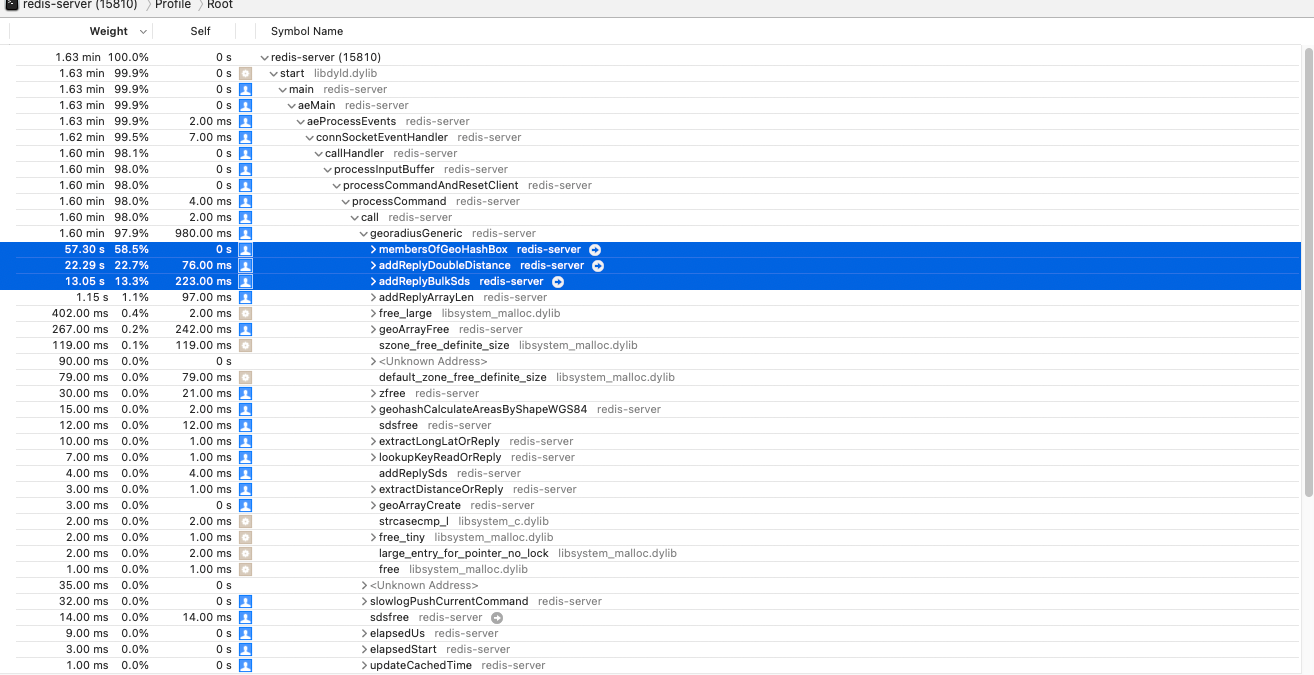
membersOfGeoHashBox
在这个函数中可以看到最费时间的 4 个函数(没按层级划分,只找到最费时的),分别为:
geohashGetDistancedecodeGeohashzmalloc_usablezfree
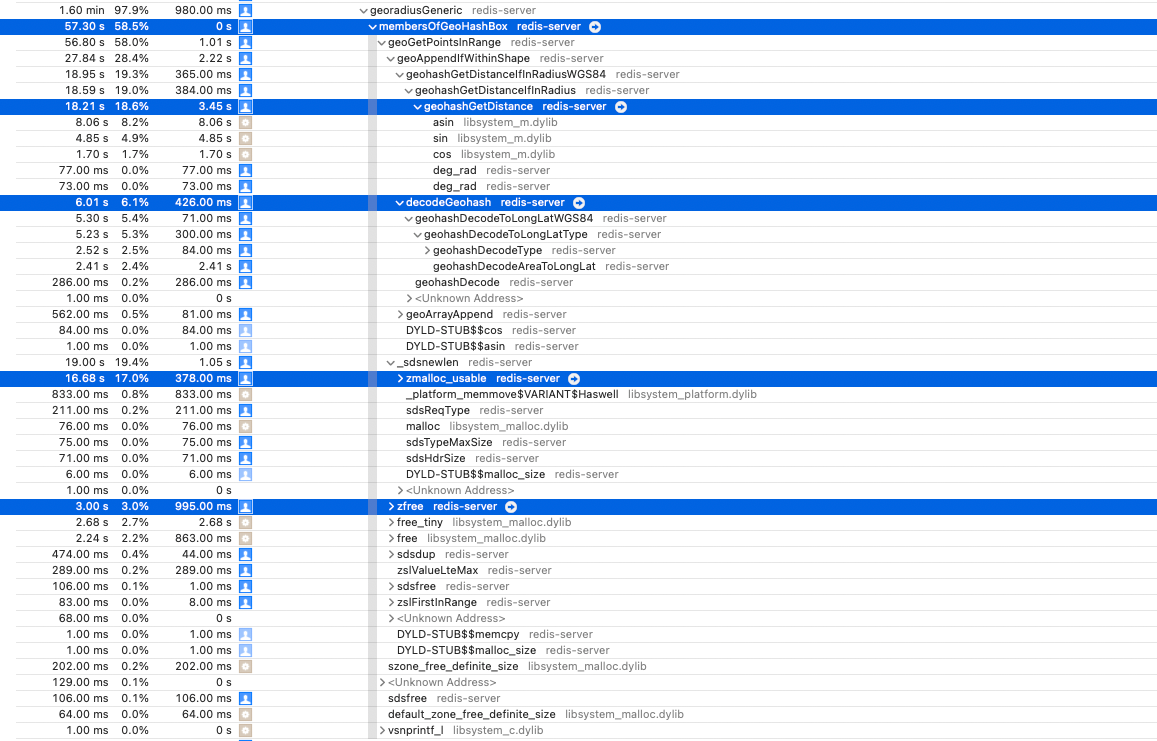
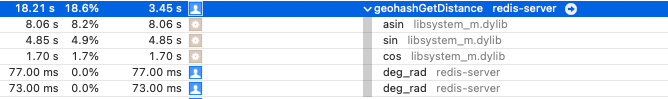
geohashGetDistance
这个函数是计算两点见经纬度的距离的,最费时间的函数是 asin 函数。
1 | // 计算两点之间的距离 |
美团解决这个计算的方案:link,这个方案的问题是如果两点之间距离远,那么误差会比较大。
下图为耗时图:
decodeGeohash
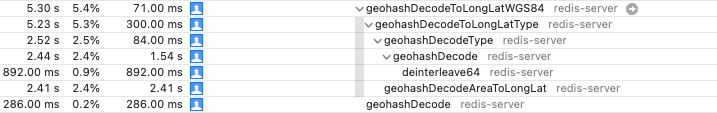
这个函数中有两个函数费时间,分别耗时:2.4% 和 2.4%,耗时原因也是因为大量的计算。但是这个计算目前没有很好的解决方案。
- geohashDecode:
这里最费时间的是将 hash 的经纬度还原的函数,将这个经纬度夹在一个很小的范围内。这个很小的范围就近似于这个点(因为 decode 也是这么算的,还原也得这还原)。
1 | int geohashDecode(const GeoHashRange long_range, const GeoHashRange lat_range, |
- geohashDecodeAreaToLongLat:
上面一个函数将点夹逼在一个很小的范围内,这个函数将夹逼的点还原(感觉整的像分析代码逻辑,本文不讲逻辑,只讲优化方案)。
1 | // 将夹逼的点还原成原来的点 |
下图为耗时图:
zmalloc&free
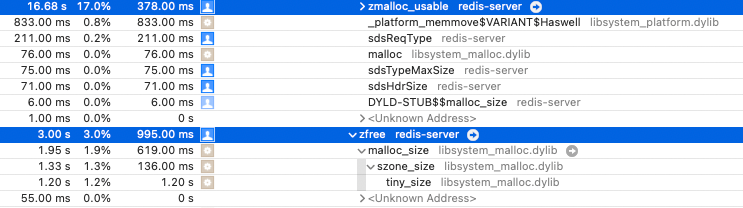
这个道理都懂,分配内存和释放内存所耗费的时间,大约耗时 20%。这里代码分析的少,感觉没有用内存池,觉得可以加一个内存池,来避免系统调用的开销?但 redis 设计者应该也想到这个方案了,他们肯定有自己的顾虑。
1 | void *ztrymalloc_usable(size_t size, size_t *usable) { |
下图为耗时图:
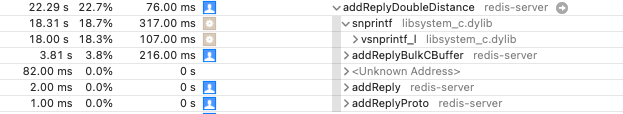
addReplyDoubleDistance
这个函数中最耗时的是调用 stdio 中的snprintf函数,耗时占 18.3%。
这个函数我觉得不能改造(天呐!怎么有人改造 stdio 中的函数)。如果要改造,通用性就不强了,如果有更好的方案欢迎聊聊。
1 | /* The default addReplyDouble has too much accuracy. We use this |
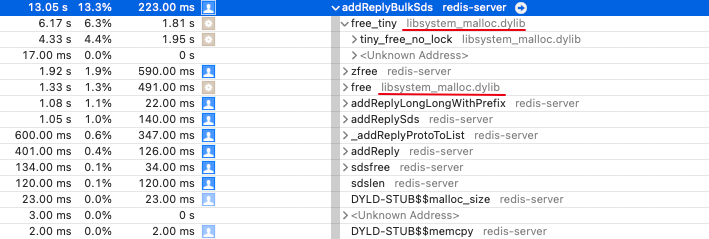
addReplyBulkSds
明显可以看出最耗时的也是库函数调用,试问,和解?我觉得无解。
总结:redis geo 性能优化方案
总的来说 redis 性能还是很 ok 的。学习代码和性能分析后,我们可以看出,redis geo 最耗时的代码主要集中在:大量的计算,库函数调用上。所以提出以下的解决方案:
- redis 层面上
- 可以采用精确度更低的计算距离的算法来提升速率。
- 针对特定的业务,可以采用自己编写的函数来提升速率(损失通用性,增加性能)。
- 调用层面上
- 可以缓存地理位置的“哈希方格”来提高效率(基本上类似于上面的
geohashDecode函数,方格大小按业务进行选择)。不建议一个点一个点缓存,基本不可能命中。白白消耗时间。
- 可以缓存地理位置的“哈希方格”来提高效率(基本上类似于上面的
- 物理层面上
(大道至简…)- 增加机器。
- 由于 redis 是单线程,每个机器上多放几个 redis,增加多核利用率。
注:本人分析的 redis 版本为测试版本(我自己的个人注释也在这里),从 redis fork 的分支。若需要分析稳定版本的请在网上自行下载。